VOXEL-MAN
The VOXEL-MAN Group of the Faculty of Medicine develops and manufactures computer-based surgery simulators for resident training, and offers them in cooperation with international partners.
Medical applications
Modern surgical techniques require manual dexterity and a thorough understanding of the surgical access paths. In order to minimize the risk for the patient, a significant training effort is required. Traditionally, surgical training is largely based on human preparates, which is increasingly reaching ethical and economic limitations.
Virtual training simulators not only overcome the lack of preparates, but offer further advantages especially for young residents. Difficult parts of an intervention may be practiced over and over again at any time, without special preparations or the need for disposable materials. The position of structures at risk can be much better understood using various visualization techniques. Through an automatic evaluation, the training success can be monitored and visualized as learning curves.
Surgery simulators already established on the market include
VOXEL-MAN ENT
, with the modules
VOXEL-MAN Tempo
for the surgical access to the middle ear and
VOXEL-MAN Sinus
for endoscopic sinus surgery. With
VOXEL-MAN My Cases
, clinical cases can be imported into the system from CT, and be prepared as training cases. For dentistry,
VOXEL-MAN Dental
is available. With
VOXEL-MAN 3D Printing
, you can create 3D prints of your virtual patient - pre-, post- and even intraoperatively. The latest development to date is
VOXEL-MAN Sonography
for training in endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) in internal medicine.
The effectiveness of our training simulators is demonstrated by numerous independent validation studies .
Technical background
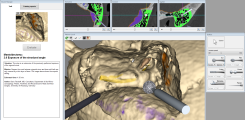
VOXEL-MAN simulators are based on methods of medical image computing, virtual reality, and robotics. The patient is modeled inside a computer based on real CT data, and displayed three-dimensionally on the screen. The surgical instruments are controlled using so-called haptic devices. Their handpieces can be moved freely in space. Through a patented haptic rendering, any contact between instruments and patient is directly perceptible, such that e.g. small bumps can be sensed very accurately, and worked on putting more or less pressure on the instrument. With simulated bleeding and a suction, two-handed work can be practiced.
The representations of the surgical site and instruments are complemented by vibrations and drilling noise. The surgery on virtual patients thus comes close to a real procedure in a visual, haptic and audible sense.
All VOXEL-MAN simulators are developed in cooperation with clinical partners at the UKE and other leading hospitals.
Further information
Today, VOXEL-MAN simulators are used at universities, public and private hospitals around the world. More information about our products can be found at www.voxel-man.com.